"THE BEST WAY TO PREDICT THE FUTURE IS TO INVENT IT." - ALAN KAY
Elemental Methods, LLC, located in Irving, Texas, is a consulting and professional services company, specializing in the design and implementation of innovative solutions. We align business processes with efficient IT systems to maximize productivity and create competitive advantage. Combining unparalleled industry and technical expertise, Elemental Methods delivers IT Next Practices, Project Leadership, Business Consulting, and Architecture Design services to clients throughout the United States. Our consulting team has significant expertise and experience in the development and hosting of systems to support customer interaction and unique customer experiences. These systems range from customer-facing websites and web portals for use by employees and consumers to self-service devices supporting customer transactions and mobile applications (iPhone, iPad, Android) driving enterprise connectivity with customers.
Our business and industry veterans are among the most capable and highly experienced in each of these competencies. Each maintains a rigorously documented and highly visible track record of success in navigating complex business scenarios in all varieties of organizational environments. Additionally, our Partner Network continuously refreshes skills and practices in order to drive maximum value for our Clients.
Elemental Methods is certified by the State of Texas as a Historically Underutilized Business (HUB ID Number 83084). We are also certified as a “Minority Business Enterprise (MBE) by the North Central Texas Regional Certification Agency (NCTRCA Certification ID Number BMMB48252N0212).
What we do
Elemental Methods provides Information Technology services focused on five areas: (1) Custom Application Development, (2) Project Management, (3) Social Media Marketing, (4) Information Technology Strategy, and (5) the Elemental Weather API.
Custom Application Development:
Elemental Methods specializes in the creation of software applications specifically designed to run on a particular computing platform or framework. A platform can be a specific operating system (such as iOS, Android, Windows), a web-based platform (like Facebook, Instagram, SnapChat, or Google), or a development framework (such as Drupal, WordPress, Shopify).
Our developers use programming languages, tools, and APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) provided by the platform to build, customize, and optimize applications that leverage the platform’s features and capabilities. These applications are tailored to meet the specific requirements and functionalities of that platform, ensuring compatibility, performance, and integration with its ecosystem. The objective is to create software that maximizes the potential of the platform while meeting the needs of our clients and their endusers.
Project Management:
At Elemental Methods, we recognize that the difference between success and failure in the implementation of technology and business process innovation is Project Management. The complexity of integrating new software, systems, and/or business processes with existing business environments requires discipline and constant oversight. Our Project Management services incorporate traditional project management techniques, along with newer project management practices, such as Agile Project Management. In all of our engagements, we implement project plans designed to monitor all project activity and communicate project status to our clients.
Elemental Methods recognizes, and stresses, the importance of having trained professionals managing client projects. Many of our Project Managers and Directors are Project Management Professionals (PMP) certified by the Project Management Institute.
Elemental Methods' project managers are trained in the use of manual techniques and automated tools to manage client engagements. The tools, techniques, and methodologies used in each engagement are determined by the complexity of the project, the client's preference for specific tools, and the client's project status reporting requirements.
Social Media Marketing:
Social media marketing refers to the use of social media platforms and networks to promote products, services, brands, or content. It involves creating and sharing engaging content on various social media channels, such as Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, LinkedIn, TikTok, and others, to reach and engage with a target audience.
Our social media marketing services include building brand awareness, increasing website traffic, generating leads, engaging with customers, and ultimately driving sales or achieving specific business objectives. The social media marketing strategies that we implement involve creating compelling content, interacting with followers, running targeted advertisements, analyzing data and metrics, and adapting tactics to optimize performance and achieve desired outcomes on social media platforms.
Information Technology Strategy:
Elemental Methods works with large enterprises and small businesses to implement new technologies in conjunction with business process innovation. Many of our clients are searching for new ways to reach new customers and interact with existing customers. They are focused on maximizing return on investment, while integrating new technologies into existing systems. They share our belief that IT projects must return value to the organization. The implementation of new technology must have a positive impact on revenue, efficiency, and/or customer satisfaction.
In the Small/Medium business market segment, Elemental Methods has been involved in the implementation of innovative solutions to enhance the competitive position of the company. From marketing support applications, to database-driven applications or comprehensive ecommerce systems, the creative implementation of technology can easily level the playing field between small and large companies. Small businesses gain the reach and efficiency of large organizations without the significant investment required in large companies.
Elemental Weather:
The Elemental Weather API is an online service providing comprehensive weather data, including current conditions, extended forecasts, and historical weather data for web and mobile applications supporting active user communities.
Available weather metrics include temperature, rainfall, wind speed (including gusts), snow, perceived temperature, humidity, and air pressure. Historical weather data is available at hourly and daily levels. Forecasts are available for hourly, daily, and 12-hour (day/night) periods.
CUSTOM APPLICATION DEVELOPMENT
How do you Plan, Build, and Run the new technologies that are critical to meeting business objectives?
Elemental Methods uses a disciplined approach to developing software. Our approach uses a broad set of practices, methodologies, and tools to develop high-quality software applications. It involves a range of activities that help ensure that the software application meets the needs of the users and stakeholders, is reliable, maintainable, and scalable, and is delivered on time and within budget.
Our application development discipline includes the following key components:
Requirements gathering: This involves understanding the needs and expectations of the users and stakeholders for the software application.
Design: Based on the requirements, the design phase involves developing the overall architecture, components, and interfaces of the application.
Development: This is the actual coding and implementation phase, where the application is built according to the design.
Testing: This involves verifying that the application works as expected and meets the requirements.
Deployment: Once the application is tested and validated, it is deployed to the production environment.
Maintenance: After deployment, the application needs to be maintained, updated, and enhanced over time to ensure it continues to meet the changing needs of the users and stakeholders.
To ensure that these components are executed efficiently and effectively, our application development teams often use agile methodologies and use various tools such as version control, issue tracking, and continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) pipelines. These practices and tools help teams to collaborate more effectively, manage code changes, and automate testing and deployment processes.
Overall, the application development discipline is essential to building high-quality software applications that meet the needs of users and stakeholders while ensuring that they are reliable, maintainable, and scalable.
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
At Elemental Methods, we recognize that the difference between success and failure in the implementation of technology and business process innovation is Project Management. The complexity of integrating new software, systems, and/or business processes with existing business environments requires discipline and constant oversight. Our Project Management services incorporate traditional project management techniques, along with newer project management practices, such as Agile Project Management. In all of our engagements, we implement project plans designed to monitor all project activity and communicate project status to our clients.
Elemental Methods recognizes, and stresses, the importance of having trained professionals managing client projects. Many of our Project Managers and Directors are Project Management Professionals (PMP) certified by the Project Management Institute.
Elemental Methods' project managers are trained in the use of manual techniques and automated tools to manage client engagements. The tools, techniques, and methodologies used in each engagement are determined by the complexity of the project, the client's preference for specific tools, and the client's project status reporting requirements.
Our project managers and consultants are trained on the following project management tools:
I/T STRATEGY CONSULTING
Information technology (IT) strategy refers to the plan or roadmap that an organization develops to use technology to achieve its business goals and objectives. An IT strategy outlines the technology initiatives and investments necessary to support the organization's overall strategy, while also providing a framework for making decisions about technology resources, architecture, and infrastructure.
We believe that a well-crafted IT strategy should align with the overall business strategy of the organization, taking into account the organization's current state of technology, industry trends, and competitive landscape. It should also consider the organization's resources and capabilities, such as budget, staffing, and infrastructure, as well as the risks and challenges associated with implementing new technology.
An IT strategy typically includes the following components:
Vision: A clear and concise statement of the desired future state of technology within the organization.
Goals and objectives: Specific, measurable, and achievable targets that the organization wants to accomplish through the use of technology.
Current state assessment: A review of the organization's existing technology infrastructure, including hardware, software, and network capabilities, to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement.
Gap analysis: An evaluation of the differences between the current state and the desired future state of technology, identifying areas where new technology investments or upgrades are needed.
Roadmap: A detailed plan outlining the steps needed to bridge the gap between the current state and the desired future state of technology, including timelines, milestones, and resource requirements.
Implementation plan: A detailed plan outlining how the technology initiatives will be implemented, managed, and monitored over time, including any necessary changes to policies, procedures, and organizational structure.
Metrics and evaluation: A set of performance metrics and evaluation criteria to measure the success of the IT strategy, including metrics for effectiveness, efficiency, and ROI.
By creating a well-defined IT strategy, Elemental Methods help organizations ensure that their technology investments align with their overall business objectives and support their growth and success.
"The empires of the future’, Winston Churchill once said, ‘are empires of the mind.’ Those words have never held more weight. Our greatest technological advances come not through physical might, tools, or cash but through intellect and imagination.”
- Jessi Hempel, Beth Kowitt - Fortune Magazine, July 26, 2010
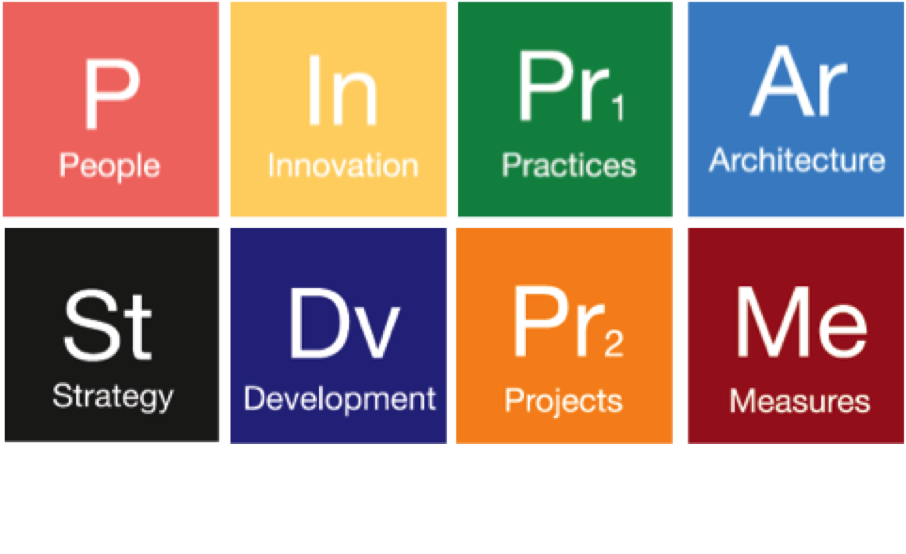
Our methodology, the "Elemental Method", clearly and uniformly represents the eight crucial factors or "elements" which must be considered, aligned, and tightly interwoven for modern businesses to successfully match increasing demand for innovation while achieving core business and technology objectives.
By taking advantage of our vast library of framework best practices and leveraging repeatable technology patterns, clients can design and implement solutions faster, at lower cost, and with less risk. The framework delivers time-tested business and technology value while maintaining several provisions for continuous improvement and ongoing enhancement. This allows many of our clients to experiment with next practices while maintaining a lower risk profile within their core technology portfolio
The delivery of services within each and/or all of these elements includes the creation and delivery of the following:
Diagnostic Tools and Measurements
Analysis and Assessment Results
Strategic Blueprint and/or Implementation Roadmap
Implementation Oversight and/or Executive Program Oversight
Projects
How does your organization manage portfolios of programs and projects? Are the outputs of projects treated as assets when the project is complete?
The accelerating rate of business change is resulting in technology projects that are more limited in scope and shorter in duration. The time between the initiation of a project and when the organization needs to realize value from that effort is decreasing. This shift to smaller project duration is enabled by service-based and component-based technologies, agile development techniques, and improved integration capabilities that allow many parts of the IT ecosystem to evolve more gradually, orchestrated through a series of smaller projects. The significance of these projects, however, does not correspond to the smaller scope and duration. Many of these projects will be initiated based solely on their positive impact on strategic objectives.
Most organizations will have "more ideas than money" in the coming years. As business processes increasingly depend on IT for process execution, having timely and meaningful management information available helps business and IT focus on projects that enable business growth and on communicating to business executives that anticipated business benefits have been delivered. With limited skills and resources, project and program prioritization will be a key concern. The development of business cases, project charters and similar tasks will be required to facilitate the ranking and prioritization of initiatives competing for funding and other resources.
Project management must be a mainstream management skill, with much of the project work elevated to specialists and watched over with significant levels of oversight. Strong consulting and system integration capabilities, with the appropriate tools and methodologies, will be critical to the successful delivery of these smaller, complex, mission-critical projects.
People
Are your People aligned with the objectives of your business?
Your most important asset in any effort will always be your people. In Information Technology, where the collaboration and communication skills are considered equally as important as technical strengths, getting the right people to the right place at the right time is absolutely critical.
During the recent recession, many companies were forced to make difficult decisions about the most efficient use of their assets - including their human assets. The shift to defensive strategies left many companies dealing with the impact of staff reductions, wage freezes, and the devalued employee incentives. Some companies used the economic crisis to redesign roles and responsibilities to improve cooperation among functions and reduce duplication of effort. These companies discovered that employees were more satisfied and more productive in a collaborative workplace.
Leadership is critical in managing the transition.
The difference between Leaders and Managers is that Leaders focus on getting the right things done. Managers focus on getting things done the right way.
Innovation
How do you enhance value creation and speed to market while managing existing products and services?
While the United States is currently rebounding from one of the most serious economic crises in history, many companies view innovation as their "investment of choice" in response to limited market growth. As traditional product and service growth opportunities mature in advanced economies, companies will seek new revenue and earnings growth from emerging markets, as well as new applications to help meet basic human demands. Government and commercial initiatives are being introduced to drive innovation in the marketplace.
The expansion of new computing and delivery models, such as Cloud Computing, will be needed to support the pace of design and introduction of new products in the market. Likewise, the development of new technologies and their incorporation into traditional environments will also create new efficiencies in the marketplace.
Elemental Methods assists clients in moving quickly to support, guide, and, in some cases, lead the implementation of new technologies in the organization. We understand that development expertise, project management discipline, and close alignment with business strategy will be critical for achieving success in technology innovation.
Architecture
Do you have a coherent infrastructure blueprint and is it sustainable? How will you manage change?
Enterprise architecture/infrastructure design and consulting fundamentally focuses on the design of business architecture and its alignment with underlying technology elements that form the foundation on which enterprise operations rely to run the IT environment. The technology surrounding this area includes a broad category of architectures and assets used to store and access data, as well as connectivity and transport.
Infrastructure and IT operations are usually the single largest portions of overall IT budgets, ranging from 60% to 70% of overall IT spending. Therefore, many companies should be investing in the analysis of their enterprise architecture and infrastructure designs to find sources of savings and/or determine the impact of new disruptive options, including virtualization, cloud computing or infrastructure utility.
The main benefit that organizations derive from architectural initiatives is an impact analysis, whereby a quantitative business case analysis of savings and an overall road map for potential changes in the enterprise architecture or infrastructure operations result. With the business case and roadmap in hand, organizations can make change decisions related to economic and budgetary realities, compliance issues and other market forces affecting their businesses. The analysis and action plan are also used to investigate and assimilate new, disruptive technologies, solutions or paradigm shifts to regain or maintain competitive parity with industry rivals, as well as gaining competitive advantage.
Strategy
Are your business and IT strategies aligned to create value? How often do you revisit your plans?
Many enterprises lack a framework to ensure business alignment with their IT strategies. Yet, sound strategy is critical for prioritizing IT projects and services.
Strategy Services facilitate the collaboration between leaders from the enterprise lines of business and functional organizations, business process owners, and business systems leads with IT stakeholders, including enterprise architects, IT service management professionals, and application development professionals. Through facilitated sessions, organizations assess their current state and set directions for software and technology that are aligned with the organizations' business objectives.
Development
How do you Plan, Build, and Run the new technologies that are critical to meeting business objectives?
Several key trends are shaping the enterprise development environment. Technology and governance advances are improving the speed, agility and quality of software delivery and the business utility of application development (AD) tools. Service-oriented development of applications (SODA) and Web-oriented architecture (WOA) are driving the alteration of methods and tools, and the convergence of runtime and development time facilities. Techniques and tools to improve the planning, measurement, control and reporting of application development and delivery activities are advancing quickly. Collaborative, cross-functional integration is being added to toolsets to help deal with the challenges of geographically distributed teams, and teams using agile methods. Other changes are being introduced to accommodate the needs of rich Internet applications and new deployment alternatives like the cloud.
As with all other IT disciplines, application development organizations are under pressure to become financially effective. Formal processes must be implemented to achieve the goal of running IT as a business, with budgeting disciplines and effective planning techniques that lead to predictable results. Although individually incremental, the convergence of changes in governance, planning and control techniques are transformative when taken across all topic areas.
Through collaborative and integration efforts, application development environments and architectures will become more efficient and cost-effective.
Practices
How does IT manage operations and are they perceived as a trusted advisor and partner to your business?
Business operations improvement practices enable lowering of operating costs and total cost of ownership (TCO), while improving the quality of services delivered and business operational process transparencies. These improvement practices assure operational compliance or the correct application of frameworks, such as Information Technology Infrastructure Library v.3 (ITIL) and ISO 20000 for delivery and support processes, and Control Objectives for Information and Related Technology (CobiT) to improve the governance of the targeted business operation.
The imperative to align to a business-value-focused strategy is obvious to many operations managers; however, the task is difficult without practices that drive collaboration, process excellence and the appropriate amount of standardization needed to reduce IT complexity. Our business operations improvement expertise encompass a wide array of consulting services offerings, such as benchmarking, certifications, performance assessments, process improvements, engineering and re-engineering of processes, skill enhancement and the application of software and technologies. These tools are critical for success in optimizing operating costs and business agility.
Measures
Does your organization regularly evaluate project progress and contribution to business objectives? What are your key performance indicators? How do you reallocate your IT investment portfolio to meet objectives?
Volatile business and market conditions are driving the implementation of transactional and systematic cost optimization initiatives in most enterprises. Benchmarking, best practices, Design of Experiments, ISO9000, Six Sigma, Total Quality Management and lean manufacturing are all process improvement methodologies that have established themselves as standard tools for transforming IT and business processes.
Establishing clear metrics is essential in evaluating milestones, understanding areas of improvement, and establishing the business relevance of IT processes and systems. Good performance metrics provide motivation for positive change, especially when the measurement process is transparent and accessible, and when the metrics are simple and well-understood.
The three most mentioned metrics used to evaluate the success of projects are: alignment to company strategy and goals, revenue growth, and cost savings to the enterprise. Without a formal strategy, defining metrics and aligning them with process maturity and investment, IT senior management lacks the foundational tools to identify the necessary investment in, and the efficiency and quality of service delivery.